Install Bitbucket Data Center
This page describes how to migrate an existing instance of Bitbucket Server to Bitbucket Data Center. For an overview, see Bitbucket Data Center resources. If you are installing Bitbucket Server instance go straight to Getting started instead. We also recommend reading Using Bitbucket Server in the enterprise. If you just want to add another node we suggest you take a look at Adding cluster nodes to Bitbucket Data Center.
This guide assumes that you already have a production instance of Bitbucket Server, and that you are aiming to migrate that to a Bitbucket Data Center instance.
We recommend that you:
- Purchase a Bitbucket Data Center license, or, obtain an evaluation license.
- Set up and test Bitbucket Data Center in your staging environment, before deploying to a production environment.
- Upgrade Bitbucket Server, and then make a backup of your production instance of Bitbucket Server.
- Restore a copy of this backup into your clustered staging environment.
- Test Bitbucket Data Center with identical data (repositories, users, add-ons) to your production instance.
Regardless of the process you use, please smoke test your Bitbucket Data Center instance every step of the way.
On this page
Overview and requirements
It's worth getting a clear understanding of what you're aiming to achieve, before starting to provision your Bitbucket Data Center.
A Bitbucket Data Center instance consists of a cluster of dedicated machines connected, and with like this:
The URL of the Bitbucket Data Center instance will be the URL of the load balancer, so this is the machine that you will need to assign the name of your Bitbucket Server instance in the DNS.
The remaining machines (Bitbucket cluster nodes, shared database, and shared file system) do not need to be publicly accessible to your users.
Bitbucket cluster nodes
The Bitbucket cluster nodes all run the Bitbucket Data Center web application.
- Each Bitbucket cluster node must be a dedicated machine.
- The machines may be physical or virtual.
- The cluster nodes must be connected in a high speed LAN (that is, high bandwidth and low latency).
- The usual Bitbucket Server supported platforms requirements, including those for Java and Git, apply to each cluster node.
- The cluster nodes do not all need to be absolutely identical, but for consistent performance we recommend they should be as similar as possible.
- All cluster nodes must run the same version of Bitbucket Data Center.
- All cluster nodes must have synchronized clocks (for example, using NTP) and be configured with the identical timezone.
- Ensure that only permit cluster nodes are allowed to connect to a Bitbucket cluster node's Hazelcast port, which by default is port 5701, through the use of a firewall and/or network segregation.
Load balancer
You can use the load balancer of your choice. Bitbucket Data Center does not bundle a load balancer.
- Your load balancer should run on a dedicated machine.
- Your load balancer must have a high-speed LAN connection to the Bitbucket cluster nodes (that is, high bandwidth and low latency).
- Your load balancer must support both HTTP mode (for web traffic) and TCP mode (for SSH traffic).
- Terminating SSL (HTTPS) at your load balancer and running plain HTTP from the load balancer to Bitbucket Server is highly recommended for performance.
- Your load balancer should support "session affinity" (also known as "sticky sessions").
If you don't have a preference for your load balancer, we provide instructions for haproxy, a popular Open Source software load balancer.
共有データベース
You must run Bitbucket Data Center on an external database. You can not use Bitbucket Server's internal HSQL or H2 database with Bitbucket Data Center.
- The shared database must run on a dedicated machine.
- The shared database must be available to all cluster nodes via a high-speed LAN (it must be in the same physical data center).
- All the usual database vendors in Bitbucket Server's supported platforms are supported by Bitbucket Data Center, with one exception: we do not recommend MySQL at this time due to inherent deadlocks that can occur in this database engine at high load.
共有ファイル システム
Bitbucket Data Center requires a high performance shared file system such as a SAN, NAS, RAID server, or high-performance file server optimized for I/O.
- The shared file system must run on a dedicated machine.
- The file system must be available to all cluster nodes via a high-speed LAN (it must be in the same physical data center).
- The shared file system should be accessible via NFS as a single mount point.
What is stored on the shared file system?
- 設定ファイル
- data directory, which includes:
- repositories
- attachments
- avatars
- plugins
What is stored locally on each node?
- caches
- logs
- temporary files
1. Upgrade your existing production instance of Bitbucket Server
Begin by upgrading your production Bitbucket Server instance to the latest public release. This is necessary for several reasons:
- The Bitbucket Server database and home directory layout often change in each release of Bitbucket Server. Upgrading first will ensure that your production Bitbucket Server instance and your Bitbucket Data Center instance share identical data format, and you can switch between them at will.
- Any add-ons in your production instance can be verified as compatible with the latest release of Bitbucket Server (or updated if not).
- Any performance or other comparisons between single-node Bitbucket Server and multi-node Bitbucket Data Center will be more meaningful.
Upgrade your Bitbucket Server by following the instructions in the Bitbucket Server upgrade guide.
2. Back up your production instance
Now, take a backup of your production Bitbucket Server instance's database and home directory. For this you can:
- use the Bitbucket Server backup client,
- use your own DIY backup solution, or
- stop Bitbucket Server and manually dump your database, and zip up the home directory.
3. Provision your shared database
Set up your shared database server. Note that clustered databases are not yet supported.
See Connecting Bitbucket Server to an external database for more information.
You must ensure your database is configured to allow enough concurrent connections. Bitbucket Server by default uses up to 80 connections per cluster node , which can exceed the default connection limit of some databases.
For example, in PostgreSQL the default limit is usually 100 connections. If you use PostgreSQL, you may need to edit your postgresql.conf file, to increase the value of max_connections, and restart Postgres.
We do not support MySQL for Bitbucket Data Center at this time due to inherent deadlocks that can occur in this database engine at high load. If you currently use MySQL, you should migrate your data to another supported database (such as PostgreSQL) before upgrading your Bitbucket Server instance to Bitbucket Data Center. You can migrate databases (on a standalone Bitbucket Server instance) using the Migrate database feature in Bitbucket Server's Adminstration pages, or by using the Bitbucket Server backup client.
4. Provision your shared file system
Set up your shared file server.
See Bitbucket Data Center FAQ for performance guidelines when using NFS.
You must ensure your shared file system server is configured with enough NFS server processes.
For example, some versions of RedHat Enterprise Linux and CentOS have a default of 8 server processes. If you use one of these systems, you may need to edit your /etc/sysconfig/nfs file, increase the value of RPCNFSDCOUNT, and restart the nfs service.
You must ensure your shared file system server has the NFS lock service enabled . For example:
- In some versions of Ubuntu Linux you must ensure that the
portmapanddbusservices are enabled for the NFSlockdto function. - In some versions of RedHat Enterprise Linux and CentOS, you must install the
nfs-utilsandnfs-utils-libpackages, and ensure therpcbindandnfslockservices are running.
Create a Bitbucket Server user account (recommended name atlbitbucket) on the shared file system server to own everything in the Bitbucket Server shared home directory. This user account must have the same UID on all cluster nodes and the shared file system server. In a fresh Linux install the UID of a newly created account is typically 1001, but in general there is no guarantee that this UID will be free on every Linux system. Choose a UID for atlbitbucket that's free on all your cluster nodes and the shared file system server, and substitute this for 1001 in the following command:
sudo useradd -c "Atlassian Bitbucket" -u 1001 atlbitbucketYou must ensure that the atlbitbucket user has the same UID on all cluster nodes and the shared file system server.
Then restore the content of directory ${BITBUCKET_HOME}/shared from the backup you have taken in step 2 into the new shared database and shared home directory.
Only the shared directory in the Bitbucket Server home directory needs to be restored into the shared home directory. The remaining directories (bin, caches, export, lib, log, plugins, and tmp) contain only caches and temporary files, and do not need to be restored.
You must ensure that the user running Bitbucket Server (usually atlbitbucket) is able to read and write everything in the Bitbucket shared home directory, both the node-local part and the shared part (in NFS). The easiest way to do this is to ensure that:
atlbitbucketowns all files and directories in the Bitbucket home directory,atlbitbuckethas the recommendedumaskof0027, andatlbitbuckethas the same UID on all machines.
Do not run Bitbucket Server as root. Many NFS servers squash accesses by root to another user.
5. Provision your Elasticsearch node
Elasticsearch is an engine that provides search functionality for Bitbucket Server.
To set up your Elasticsearch server, following the instructions on the page Install and configure a remote Elasticsearch instance.
6. Provision your cluster nodes
We highly recommend provisioning cluster nodes using an automated configuration management tool such as Chef, Puppet, or Vagrant, or by spinning up identical virtual machine snapshots.
On each cluster node, mount the shared home directory as
${BITBUCKET_HOME}/shared. For example, suppose your Bitbucket home directory is/var/atlassian/application-data/bitbucket, and your shared home directory is available as an NFS export calledbitbucket-san:/bitbucket-shared. Add the following line to/etc/fstabon each cluster node:/etc/fstabbitbucket-san:/bitbucket-shared /var/atlassian/application-data/bitbucket/shared nfs lookupcache=pos,noatime,intr,rsize=32768,wsize=32768 0 0Only the
${BITBUCKET_HOME}/shareddirectory should be shared between cluster nodes. All other directories, including${BITBUCKET_HOME}, should be node-local (that is, private to each node).Bitbucket Data Center checks during startup that
${BITBUCKET_HOME}is node local and${BITBUCKET_HOME}/sharedis shared, and will fail to form a cluster if this is not true.Your shared file system must provide sufficient consistency for Bitbucket Server and Git.
Linux NFS clients require the
lookupcache=posmount option to be specified for proper consistency.Then mount it:
mkdir -p /var/atlassian/application-data/bitbucket/shared sudo mount -aEnsure all your cluster nodes have synchronized clocks and identical timezone configuration. For example, in RedHat Enterprise Linux or CentOS:
sudo yum install ntp sudo service ntpd start sudo tzselectIn Ubuntu Linux:
sudo apt-get install ntp sudo service ntp start sudo dpkg-reconfigure tzdataFor other operating systems, consult your system documentation.
The system clocks on your cluster nodes must remain reasonably synchronized (say, to within a few seconds or less). If your system clocks drift excessively or undergo abrupt "jumps" of minutes or more, then cluster nodes may log warnings, become slow, or in extreme cases become unresponsive and require restarting. You should run the NTP service on all your cluster nodes with identical configuration, and never manually tamper with the system clock on a cluster node while Bitbucket Data Center is running.
Download the latest Bitbucket Data Center distribution from https://www.atlassian.com/software/bitbucket/download, and install Bitbucket Server as normal on all the cluster nodes. See Install Bitbucket Server on Linux from an archive file or Install Bitbucket Server on Windows from a zip file for installation instructions.
7. Start the first cluster node
Edit the file ${BITBUCKET_HOME}/shared/bitbucket.properties , and add the following lines:
# Use multicast to discover cluster nodes (recommended).
hazelcast.network.multicast=true
# If your network does not support multicast, you may uncomment the following lines and substitute
# the IP addresses of some or all of your cluster nodes. (Not all of the cluster nodes have to be
# listed here but at least one of them has to be active when a new node joins.)
#hazelcast.network.tcpip=true
#hazelcast.network.tcpip.members=192.168.0.1:5701,192.168.0.2:5701,192.168.0.3:5701
# The following should uniquely identify your cluster on the LAN.
hazelcast.group.name=your-bitbucket-cluster
hazelcast.group.password=your-bitbucket-clusterUsing multicast to discover cluster nodes (hazelcast.network.multicast=true) is recommended, but requires all your cluster nodes to be accessible to each other via a multicast-enabled network. If your network does not support multicast then you can set hazelcast.network.multicast=false, hazelcast.network.tcpip=true, and hazelcast.network.tcpip.members to a comma-separated list of cluster nodes instead. Only enable one of hazelcast.network.tcpip or hazelcast.network.multicast, not both.
Choose a name for hazelcast.group.name and hazelcast.group.password that uniquely identifies the cluster on your LAN. If you have more than one cluster on the same LAN (for example, other Bitbucket Data Center instances or other products based on similar technology such as Confluence Data Center) then you must assign each cluster a distinct name, to prevent them from attempting to join together into a "super cluster".
Then start Bitbucket Server. See Starting and stopping Bitbucket Server.
Then go to http://<bitbucket>:7990/admin/license, and install your Bitbucket Data Center license. Restart Bitbucket Server for the change to take effect. If you need a Bitbucket Data Center license, you can purchase one that fits your needs, or, get an evaluation license.
8. Install and configure your load balancer
You can use the load balancer of your choice, either hardware or software. Bitbucket Data Center does not bundle a load balancer.
Your load balancer must proxy three protocols:
| プロトコル | Typical port on the load balancer | Typical port on the Bitbucket cluster nodes | 注意 |
|---|---|---|---|
| http | 80 | 7990 | HTTP mode. Session affinity ("sticky sessions") should be enabled using the 52-character BITBUCKETSESSIONID cookie. |
| HTTPS | 443 | 7990 | HTTP mode. Terminating SSL at the load balancer and running plain HTTP to the Bitbucket cluster nodes is highly recommended. |
| ssh | 7999 | 7999 | TCP mode. |
Your load balancer must support session affinity ("sticky sessions") using the BITBUCKETSESSIONID cookie. Bitbucket Data Center assumes that your load balancer always directs each user's requests to the same cluster node. If it does not, users may be unexpectedly logged out or lose other information that may be stored in their HTTP session.
When choosing a load balancer, it must support the HTTP, HTTPS, and TCP protocols. Note that:
- Apache does not support TCP mode load balancing.
- HAProxy versions older than 1.5.0 do not support HTTPS.
If your load balancer supports health checks of the cluster nodes, configure it to perform a periodic HTTP GET of http:// <bitbucket>:7990/status, where <bitbucket> is the cluster node's name or IP address. This returns one of two HTTP status codes:
- 200 OK
- 500 Internal Server Error
If a cluster node does not return 200 OK within a reasonable amount of time, the load balancer should not direct any traffic to it.
You should then be able to navigate to http://<load-balancer>/, where <load-balancer> is your load balancer's name or IP address. This should take you to your Bitbucket Server front page.
Example: HAProxy load balancer
If you don't have a particular preference or policy for load balancers, you can use HAProxy which is a popular Open Source software load balancer.
If you choose HAProxy, you must use a minimum version of 1.5.0. Earlier versions of HAProxy do not support HTTPS.
To check which version of HAProxy you use, run the following command:
haproxy --version
Here is an example haproxy.cfg configuration file (typically found in the location /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg). This assumes:
- Your Bitbucket cluster node is at address 192.168.0.1, listening on the default ports 7990 (HTTP) and 7999 (SSH).
- You have a valid SSL certificate at
/etc/cert.pem.
global
pidfile /var/run/haproxy.pid
maxconn 4000
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
tune.ssl.default-dh-param 1024
defaults
log global
option dontlognull
option redispatch
retries 3
timeout http-request 10s
timeout queue 1m
timeout connect 10s
timeout client 1m
timeout server 1m
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
maxconn 3000
errorfile 408 /dev/null # Workaround for Chrome 35-36 bug. See http://blog.haproxy.com/2014/05/26/haproxy-and-http-errors-408-in-chrome/
frontend bitbucket_http_frontend
bind *:80
bind *:443 ssl crt /etc/cert.pem ciphers RC4-SHA:AES128-SHA:AES256-SHA
default_backend bitbucket_http_backend
backend bitbucket_http_backend
mode http
option httplog
option httpchk GET /status
option forwardfor
option http-server-close
appsession BITBUCKETSESSIONID len 52 timeout 1h
balance roundrobin
cookie BITBUCKETSESSIONID prefix
stick-table type string len 52 size 5M expire 30m
stick store-response set-cookie(BITBUCKETSESSIONID)
stick on cookie(BITBUCKETSESSIONID)
server bitbucket01 192.168.0.1:7990 check inter 10000 rise 2 fall 5
#server bitbucket02 192.168.0.2:7990 check inter 10000 rise 2 fall 5
# The following "backup" servers are just here to show the startup page when all nodes are starting up
server backup01 192.168.0.1:7990 backup
#server backup02 192.168.0.2:7990 backup
frontend bitbucket_ssh_frontend
bind *:7999
default_backend bitbucket_ssh_backend
timeout client 15m
maxconn 50
backend bitbucket_ssh_backend
mode tcp
balance roundrobin
server bitbucket01 192.168.0.1:7999 check port 7999
#server bitbucket02 192.168.0.2:7999 check port 7999
timeout server 15m
listen admin
mode http
bind *:8090
stats enable
stats uri /Review the contents of the haproxy.cfg file carefully, and customize it for your environment. See http://www.haproxy.org/ for more information about installing and configuring haproxy.
Once you have configured the haproxy.cfg file, start the haproxy service.
sudo service haproxy startYou can also monitor the health of your cluster by navigating to HAProxy's statistics page at http://<load-balancer>:8090/. You should see a page similar to this:
9. Configure Tomcat/Bitbucket for HAProxy
Bitbucket needs to be configured to work with HAProxy. For example:
server.proxy-name=bitbucket.company.com
server.proxy-port=443
server.secure=true
server.require-ssl=true
Securing Bitbucket behind HAProxy using SSL for more details.
10. Add a new Bitbucket cluster node to the cluster
Go to a new cluster node, and start Bitbucket Server. See Starting and stopping Bitbucket Server.
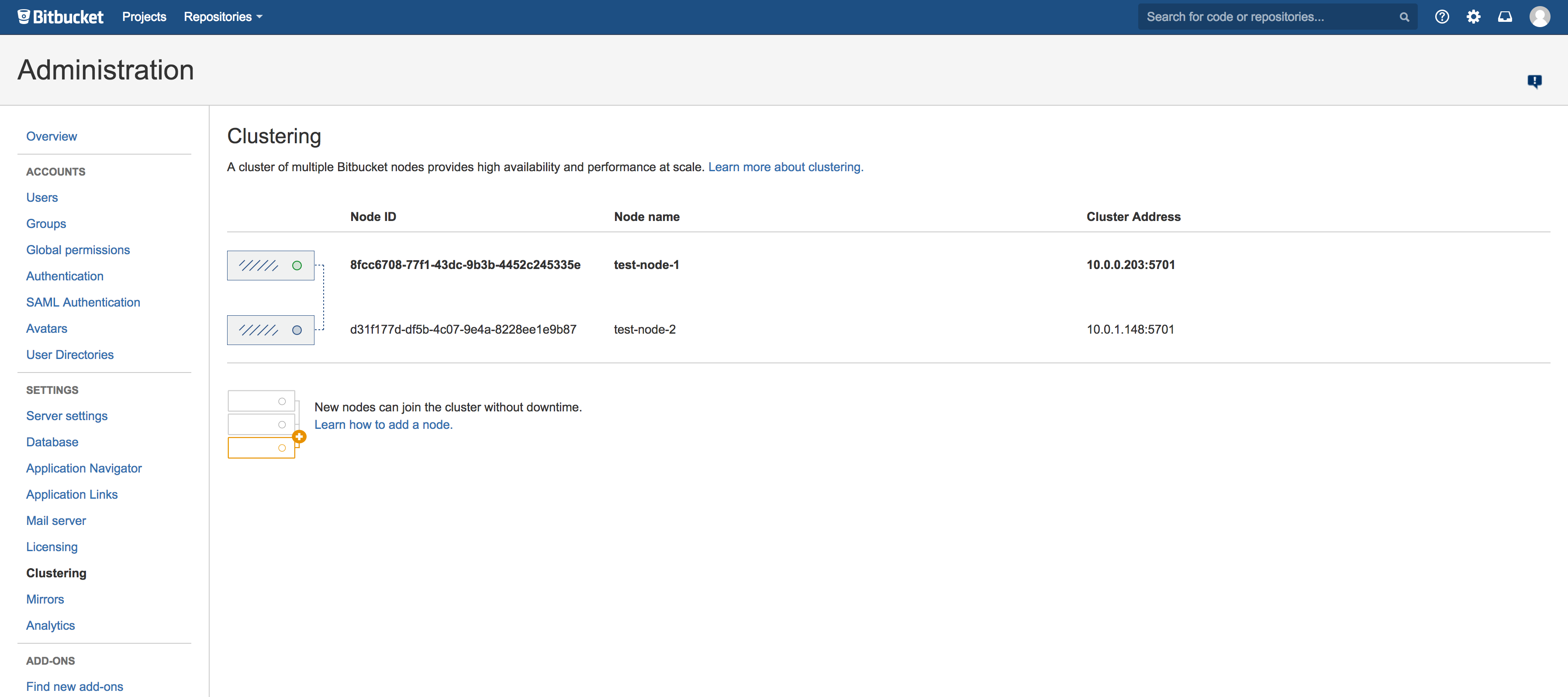
Once Bitbucket Server has started, go to
https://<load-balancer>/admin/clustering. You should see a page similar to this:
Verify that the new node you have started up has successfully joined the cluster. If it does not, please check your network configuration and the ${BITBUCKET_HOME}/log/atlassian-bitbucket.log files on all nodes. If you are unable to find a reason for the node failing to join successfully, please contact Atlassian Support .
11. Connect the new Bitbucket cluster node to the load balancer
If you are using your own hardware or software load balancer, consult your vendor's documentation on how to add the new Bitbucket cluster node to the load balancer.
If you are using HAProxy, uncomment these lines
server bitbucket02 192.168.0.2:7990 check inter 10000 rise 2 fall 5server bitbucket02 192.168.0.2:7999 check port 7999in your haproxy.cfg file and restart haproxy:
sudo service haproxy restartVerify that the new node is in the cluster and receiving requests by checking the logs on each node to ensure both are receiving traffic and also check that updates done on one node are visible on the other.
12. Repeat steps 10 and 11 for each additional cluster node
Congratulations!
You have now set up a clustered instance of Bitbucket Data Center! We are very interested in hearing your feedback on this process – please contact us!
For any issues please raise a support ticket and mention that you are following the 'Installing Bitbucket Data Center' page.
Please see Using Bitbucket Server in the enterprise for information about using Bitbucket Server in a production environment.